 |
| 11 SEO Mistakes and How To Fix Them |
Most webmasters pay too little attention to on-site optimization or do not have sufficient knowledge. Digital marketing pro-SEMrush created a global study on the subject. Real data was used, more than 100,000 domains and around 450 million pages were analyzed and the 11 most common on-site problems were identified.
Onsite Mistake 1: Duplicate Content
Google defines duplicate content as "large blocks of content that correspond or are strikingly similar to other content on the same or different domain". According to the SEMrush study, 50% of websites have duplicate content. Thus, this problem occurs particularly frequently and is in 1st place.
In the current Google Q&A session, it was pointed out that there is no duplicate content penalty. With duplicate content, the webmaster can no longer decide which page should rank and which should not, which is a landing page, and which was created for the visitors. In addition, search engines prefer pages that offer unique content.
Short tips and solutions:
- Merge the same pages or delete duplicates;
- Use the "rel=canonical" tag if no technical intervention is possible;
- use 301 redirects;
- "noindex" meta tags;
- Disallow in robots.txt;
- Google Search Console (parameter setting).
- Important: The points should not be combined with each other.
Further tips:
The correct spelling of the links is probably the most common source of errors. If you have selected the main domain without "www" in the Search Console, the address without "www" must also be specified for the internal link. Better yet, use the relative paths. One should not copy other people's texts (excluding quotations). Originality is key when it comes to content. Plagiarism should be strictly avoided at all costs.
Also Read: 9 Proven Tactics to Increase Clicks on Your Google Ads
Onsite Mistake 2: Missing Alt Tags or Images
Images are an important part of content marketing. They are also part of the SEO strategy. 45% of all pages have no or an empty alt tag. 10% of the pages have no images. Alt tags are used to display an alternative description of the image if it failed to load.
Alt tags affect image search, where they are just one of the many ranking factors. That's why you should put the keywords in the alt tags. In addition, the lack of images can hurt the conversion rate in the case of an online shop.
Short tips and solutions:
- Generate alt tags automatically or have them written manually
- Constantly scanning for missing images (important for online shops);
- Use plugins, addons, etc. depending on the CMS.
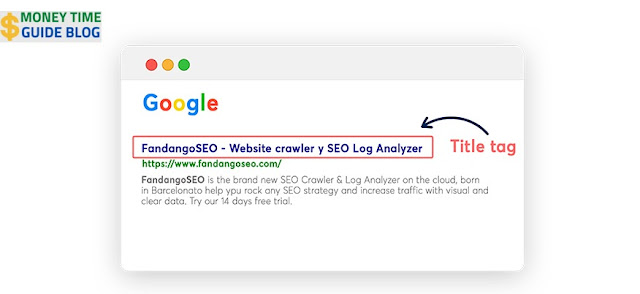
Onsite Mistake 3: Title Tag
11 SEO Mistakes and How To Fix Them
The title tag provides search engines with information about the topic of the page. Google actively uses it to determine the relevance of the page to the search query. In practice, the content of the tag is very often displayed as a heading in the search results. At this point, you should neither overestimate nor underestimate the weight of the title tag in the algorithm or only fill the title tag with keywords.
The results of the study show the 4 most common title tag errors:
- 35% of sites had duplicate title tags;
- 15% too long title tags;
- 8% no title tags at all;
- 4% too short title tags.
The title tag is one of the most important factors for ranking and influences the CTR in the search results.
A few tips and solutions:
- In the case of double title tags, the cause is often the duplicate content (see point 1);
- Title tags should not be too short (e.g. one word) and not too long (over 70 characters desktop, mobile can be less);
- Write meaningful and relevant title tags;
- The main keyword should be near the beginning of the title tag.
Read Article: TikTok Marketing: WHAT IS TIKTOK Marketing? IS TIKTOK MARKETING WORTH IT?
Onsite Mistake 4: Meta Descriptions
This meta tag describes the content of each page. Try to keep the content within 160 characters for optimal performance.
For blogs, the length can be shorter because of the article date and in some languages because of the width of the letters. Meta Description directly affects CTR and has no real meaning for ranking. According to the SEMrush study, 30% of pages had duplicate descriptions and 25% of pages had no descriptions at all.
More tips and solutions:
- Proceed with the double descriptions as with the double title tags;
- Write descriptions no longer than 160 characters (including spaces);
- Create an interesting and relevant description of the page;
- The keywords are not necessary for the description.
Onsite Mistake 5: Dead Links
With websites that are constantly growing, dead links can become a big problem. The problem gets even bigger when there are a lot of dead links and the 404 page is not set up properly. According to the SEMrush study, 35% of the examined pages have dead internal links, of which 70% are 404 links. 25% of websites have outbound links that are broken.
Dead links clearly hurt the visitor experience. Nobody wants to find out when they click on a link that the page doesn't exist. They can also hurt the distribution of link juice. Link juice is a collective term for link strength and is one of the factors used to calculate page relevancy. A page that is not linked cannot be indexed.
Short tips and solutions:
- Crawl the website regularly and fix all 404 errors;
- Pay attention to the correct spelling of the links;
- Contact technical support for 50X errors.
More Article: THE ULTIMATE INSTAGRAM ADS GUIDE
Onsite Mistake 6: Low Text-to-Code Ratio
The text-to-code ratio shows the ratio of text content to source code on a single page. 28% of all examined pages have a too-low text-to-code ratio. A low text-to-code ratio has no direct effect on the page's ranking. However, it can be a possible signal of clean code, user experience, and relevance.
Because more text results in a better ratio and theoretically a higher probability of relevance to the visitor's search query. However, one should not overstate this problem. For example, online stores often have a very low text-to-code ratio and this does not affect their rankings.
Short tips and solutions:
- Check the source code. Best with the W3C validator;
- Manually check the content on the pages. This can have a positive effect on the user experience and thus probably also on the conversion rate.
Onsite Mistake 7: H1 Heading
20% of the analyzed websites have multiple H1 headings within one page. The other 20% are missing H1 headings and 15% have an identical title tag and H1 on a single page. The H1 heading is a structure and markup element for the content on a single page. The H1 heading is one of the possible factors search engines use to determine the relevance of the document to the search query. It is also an important element of the visitor experience as it is often the first thing the visitor sees.
Short tips and solutions:
- Don't write pure SEO headlines;
- Write the headings clearly and understandably for the visitors;
- Keywords are allowed, but not mandatory;
- If possible, only use one H1 heading per page
- H1 heading and title tag should ideally be similar (identical is also no problem)
Read More Article: Is online marketing worth it for you? Pros and cons of digital advertising
Onsite Mistake 8: Word count too low
This metric counts the number of words within a page. The results of our study show that approximately 18% of websites have an under-word count on some individual pages. The question here, which is probably also relevant to the Panda update, is whether the word count on most pages of a webpage is too low or not.
If this is the case, it can be an indication of the poor quality of the entire website. If it's in a healthy proportion to the total number of pages, there's nothing to worry about. However, the question still remains as to whether more relevant content is made available to the visitor.
Short tips and solutions:
- Create good and relevant content;
- It is best to write about one topic and not all topics;
- Do not artificially inflate the text with filler words.
Onsite Mistake 9: Too Many Outbound Links on a Single Page
As the title suggests, it's about the total number of all outbound links on a single page. The number of links has an effect on the so-called link juice. To put it simply: the more links there are on a page, the less link juice is passed on to the individual linked pages. 15% of websites have too many outbound links on a single page.
Google used to recommend a maximum of 100 links in its guidelines. Today, this policy is no longer relevant. If the entire site was not created as a spam project and the links were structured and placed for the sake of visitor experience, there is nothing to worry about. So it remains a question of the sensible use of the links.
Short tips and solutions:
- Check the pages with too many links (above average);
- Technical errors are not uncommon;
- Often there are duplicate links (at the top of the menu and at the bottom of the footer).
May Read Also: Top 3 prejudices against online marketing agencies: What is behind them?
Onsite Mistake 10: Incorrect language definition
As our study shows, 12% of the websites examined either provided the wrong language specification or did not specify it at all. With the language definition in the <head> area of the website, the search engines are given an indication of the language of the website or an individual document.
Like the W3C declaration <html lang="en">, there is also the hreflang attribute advertised by Google. This information is particularly important if you operate a website with a lot of international content. If the information is missing, the search engine tries to recognize the language automatically.
Onsite Mistake 11: Permanent (301) and Temporary (302) redirects

11 SEO Mistakes and How To Fix Them
The forwarding is a signal for the search engines that the page can no longer be found at the old address but at the new address. 301 redirect is permanent. 302 redirect is temporary. If you use the 302 redirects, it is a signal to Google that it is time-limited.
As a result, the old address of the page is not removed from the index and the new page is not indexed at all. Even though there are numerous discussions about 302 redirects. Play it safe! Only use 301 redirects if the site really has moved forever.
Read More: Social media trends and their potential
Conclusion
There are still a great many websites affected by critical onsite errors. If your website is also affected by one or more of the errors described above, you now know what the problem is, what effects it has, and what you can do about it. Danger recognized danger averted!

