 |
| How to trade CFDs on stocks and cryptocurrencies |
CFD - Contract for Difference (contract based on price difference), which allows you to trade assets and make a profit without physically buying the underlying asset.
CFD is a derivative product. When trading a CFD, you get the price difference between the opening price and the closing price of the contract. An impressive CFD bonus is earnings on the price movement, which can move in any direction. In this case, profit or loss depends on the correct forecast.
Most CFD providers for trading cryptocurrencies, stocks, indices, and other assets are market makers (brokers). They create market volume. The fact is that most investors trade in small volumes, insufficient to work on the exchange, where institutional investors buy and sell for big money. And to help small participants earn on stocks, bonds, indices, raw materials, and cryptocurrencies, the broker created the mechanism of CFD contracts - a “synthetic” market for small investments.
Long and short
CFD trading allows you to earn on price movements that go up or down. Thus, you can make a profit both on the growth and on the decline of quotes.
In the first case, this is a purchase - opening a long position.
In the second - selling, or opening a short position. For example, you are convinced that security will fall in price. Then you sell CFDs on your paper. You will still receive the price difference between the opening and closing of the position but will make a profit if the stock falls and make a loss if the stock rises.
For both longs and shorts, profit or loss is realized after the position is closed.
 |
| How to trade CFDs on stocks and cryptocurrencies |
How to earn on CFDs? Shoulder Strength
Leverage means the money that the broker lends to the investor so that he can realize the transaction in a larger volume.
Leverage is a chance to earn more profit from the broker's credit funds. You can make a deal for a larger volume without paying the full cost of the purchased assets. Let's say you wanted to open a position equivalent to 500 shares of Apple. In a normal transaction, this would mean paying the full price of the shares upfront. Leverage 1:20 — the ability to pay only 5% of the cost.
At the same time, it is important to remember that profit/loss is calculated based on the entire position, and the size of the leverage is not important. Both profit and loss can be significantly higher than the cost of the transaction. Losses may be more than your deposit. Therefore, it is worth looking at the leverage ratio and monitoring the situation so as not to go beyond your real capabilities.
Margin trading
Leveraged investing is sometimes referred to as margin investing because the money to open and maintain a position up to date - "margin" - is only a fraction of the total cost.
When you open a position, you need a deposit margin, while a maintenance margin is needed when trade approaches a losing position that is not covered by the deposit margin and other funds in the account. If this happens, you may receive a margin call from your broker asking you to fund your account. The account must be replenished in the required amount, otherwise, the position will be forcibly curtailed and losses will be fixed.
Hedging
CFDs are used, among other things, to protect against risks.
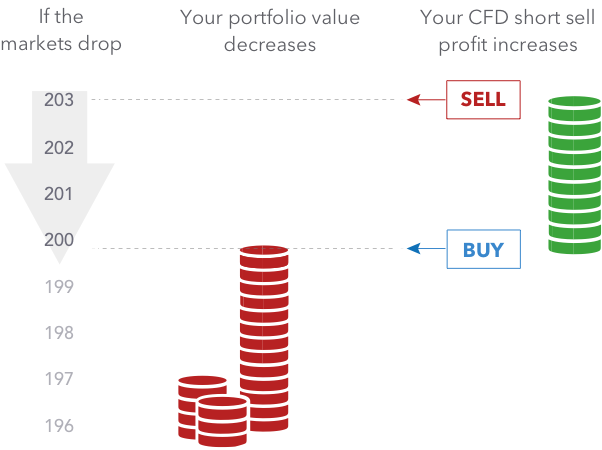 |
| How to trade CFDs on stocks and cryptocurrencies |
Suppose there is a belief that a previously purchased security may sink for a short time, for example, as a result of negative news about a hacker attack and theft of money from wallets. So, you can compensate for some of the potential losses by opening a short trade through CFD.
If you decide to protect yourself from risks using this model, any decrease in the price of a crypto asset will be offset by the income from shorting using CFDs.
How do CFDs work?
There are four key components to the CFD price structure.
1. Spread and commission
Prices are presented in terms of purchase and sale prices (Bid and Ask).
Contract purchase price (Bid) — open a short position.
Contract selling price (Ask) — open a long position.
Selling prices are slightly lower than the current market price while buying prices will be slightly higher. This slight difference is the spread.
 |
| How to trade CFDs on stocks and cryptocurrencies |
2. Contract size
CFDs are traded in standard lots. The size of an individual contract depends on the underlying asset, often mimicking the dynamics of the underlying asset.
Exchange-traded silver, for example, trades in lots of 5,000 troy ounces, and its equivalent CFD also has a value of 5,000 troy ounces.
For share CFDs, the contract size is usually one share of the company you are trading.
3. Contract expiration date (expiration)
Almost all CFDs do not have a hard expiration date. Instead, the position is closed by placing a trade in the opposite direction (opposite of the opening). For example, a position to buy 500 gold contracts would be closed by selling 500 contracts.
If you, for example, continue to hold a daily CFD position open after the close of the session, you will be charged a fee. The fee reflects the value of the capital your broker lends to you to open a leveraged trade.
This is not the case with all contracts. For example, in the case of a forward contract, it expires at a fixed point in the future and all overnight financing fees are already included in the spread.
4. Profitable and unprofitable situations
Profit or loss = number of contracts x (price at which the contract was closed − Price at which the contract was opened)
The formula above shows the net result for long CFD positions. If you are interested in calculating the result when opening short positions, simply swap the closing and opening prices of the contract.
To fully calculate the trading result, you need to subtract all commissions. These can be, for example, fees for holding or transferring a position by a broker.
What are the benefits of CFDs?
 |
| How to trade CFDs on stocks and cryptocurrencies |
1. The ability to protect positions in difficult market situations and even earn on market drawdowns.
2. CFD is trading with leverage and the ability to control a large position size with relatively small trading capital. So, if the stock margin is 10% and your deposit is $1,000, you can buy up to $10,000 worth of securities.
3. Access to many markets from a single trading account.
- Indices
- Bonds
- Agricultural products
- Products
- Precious metals
- Crypt
Trading risks in CFD trading
The main risk is leverage.
Full list of potential risks:
- the threat that the counterparty will let you down;
- incorrect forecasting of price movements;
- unexpected margin increase;
- premature triggering of a stop order.
The threat that the counterparty will let you down
Unlike shares traded in an exchange format, CFDs are traded outside the exchange market. If you are trading CFDs, it is important to find a good and trusted broker with good experience and reviews.
Mispredicting Price Movement
To invest with CFDs, you must deposit a margin that will cover your potential losses. But there are times when the market moves too fast, and in such a situation, you can lose your trading capital. If this happens, you will be required to return the margin money that you borrowed from the broker. Just in case, let's clarify that this applies not only to CFD trading but to all products with leverage.
Unexpected Margin Increase
Let's say you bought $10,000 worth of oil at a 20% margin. You need at least $2,000 in your CFD account. But during periods of volatility, your broker can raise margins up to 40%. This means that you must invest more capital to hold the $10,000 position. Otherwise, your position will be partially or completely closed (to meet margin obligations).
Premature stop action
In CFD trading, a price divergence situation may occur.
For example, the stock exchange might show $100 per Apple share, but the broker would show $101. That is, you can get a stop order in transactions, which would not be the case if you were trading on the stock exchange.
Costs in CFD trading
- Commission
- Spread
- Position holding costs
- Market Data
Commission
The commission is a fixed price for the transaction.
This is usually a % of the trade or a minimum amount, such as $10 or $20.
AMarkets allows you to trade with minimal commissions and the tightest spreads and also guarantees the expiration of the contract without forced closing of transactions.
Spread
This is the difference between the buying and selling prices. For example, the purchase price of a security is $100 and the sale price is $99.
Buy paper now - pay $100. Sell Now - $99.
The $1 spread is the cost incurred by the trader.
Experienced investors advise avoiding markets with low liquidity - there is always a large spread.
Position holding costs
This is what you pay to fund your account with a broker for each day you hold a position.
How does it work? Let's say you have $1,000 in your account and you borrow $9,000 as a margin to buy $10,000 worth of stock.
Interest is charged on the $9,000 you borrowed from the company where you opened the brokerage account.
Market Data
These are recurring costs for regularly receiving quotes and other market information.
Reliable Broker
When choosing a broker, be guided by the criteria:
- Who regulates the company? Where is the broker registered? Who checks the activity of the broker? For example, AMarkets is a member of The Financial Commission, an independent organization that regulates disputes between market participants and provides protection for each client in the amount of up to €20,000 per claim.
- Helpdesk efficiency.
- Ease of withdrawal.
- Availability of markets and assets that you are interested in.
- Special conditions that improve the investment process. For example, AMarkets offers all its clients trading signals and analytics from the best experts, personal support from a manager, and a 20% welcome trading bonus on a deposit.
Can I make money trading CFDs?
CFD trading - access to instruments that would not be available if it were not for CFDs. Can I earn on CFDs? Undoubtedly!
For efficient trading of CFDs on crypto, stock contracts, and other assets, follow this plan:
- Develop a trading strategy. Study the market, decide on the assets you will trade and the trends, and the correct forecast which will determine your trading result.
- Stick to your chosen trading strategy.
- Regularly follow the news background and prices.
- Manage risk with stops and limits.
- Diversify your portfolio by adding promising assets and removing those that are no longer interesting.
- Keep track of open positions.
- If you predict the trend incorrectly, take the loss immediately so as not to increase the losses due to unproductive waiting for the moment of reversal.
- Practice in safe mode on a demo account.
How to trade crypto CFDs using Bitcoin as an example?
Cryptocurrency CFD trading is an opportunity to earn on the exchange rate difference of digital assets. At the same time, you do not need to own coins, store them in a crypto wallet or pay commissions to a third party for storing coins. Unlike ETFs, crypto CFDs also give you the freedom to choose your coins. You buy only those assets that you consider the most promising.
At the same time, special terminals are not required for crypto CFD trading. Crypto can be bought on MT4 or MT5 - where you buy currency, stocks, and other assets.
 |
| How to trade CFDs on stocks and cryptocurrencies |
Let's give an example of CFD transactions for cryptocurrencies using the example of the flagship coin - Bitcoin.
Imagine Bitcoin with a bid price (Bid) of $27.59 and a sale price (Ask) of $27.60.
Bitcoin CFDs. Scenario #1
You think the price of BTC will rise, so you go long 2,000 CFDs at $27.60. This is equivalent to buying 2000 BTC.
If the BTC margin ratio is 5%, then your margin will be 5% of the total risk of your trade (2,000 CFD x $27.6 = $55,200), which is $2,760.
Everything is going as you predicted - the price of BTC is growing. You decide to close your position, for example at $29.60, and therefore sell your 2000 CFDs (Bitcoin) for $29.60. In this case, your profit on one CFD contract will be ($29.60 − $27.60 = $2).
For 2,000 crypto CFDs, you will earn a profit of $4,000.
But if your forecast does not come true, and the price of BTC starts to fall rather than grow, then in such a situation you want to minimize losses and, for example, sell your 2000 CFD (Bitcoin) for $26.60. Your position has moved $1 against you. So your loss is $2,000.
Bitcoin CFDs. Scenario #2
You think the price of BTC will fall, so you go short 2000 CFD (Bitcoin) at $27.59.
If BTC Margin Ratio = is 5%, then your margin will be 5% of the total risk of your trade (2,000 CFD x $27.59 = $55,180), which is $2,759.
The price of BTC is declining in line with your forecast. You decide to close the trade by buying a crypto CFD at $26.60. Your total profit on this trade will be (27.59 − 26.60) x 2000 = $1940.
But if the BTC price rises instead of falling, you will incur losses. To minimize losses, for example, you buy a CFD (Bitcoin) for $29.60. Your loss on the trade will be (29.60 − 27.59) x 2000, which is about $4020.
Thus, contracts for difference with leverage (CFDs on cryptocurrencies and other assets) can both increase your profits and lead to losses. Therefore, you need to take precautions (stops, risk management) and not bet big on trends that you are not completely sure about.
Why is it important to choose the right CFD broker through which you will trade crypto CFDs?
How did CFDs on crypto come into circulation?
Between 2016 and 2018 there was a powerful bullish trend in the digital asset segment. Therefore, many brokers have started to include cryptocurrencies in their range of CFD products. But then came 2020, a pandemic, a bearish trend, a collapse in prices, and a very uncertain recovery.
What do brokers think about crypto CFDs?
Not all brokers believe in crypto CFDs, believing that this derivative does not generate large volumes, such as, for example, EURUSD, S&P 500, or gold. This is a pretty weak argument when you take into account the fact that the number one crypto exchange, Binance, generates at least $50 billion in turnover daily from crypto derivatives alone.
Most likely, not all brokers actively promote crypto CFDs due to insufficient knowledge of the product. Many brokers have added CFDs on crypto (and only a few of the most capitalized coins) to their pool of offers solely for the show, without a clear understanding of how a trader can make money on a Bitcoin or Tether derivative.
Also, not knowing how to manage risk in this new asset class, some brokers simply increased the spreads. Many of the CFDs offered on the brokerage market are still not traded on weekends, which is completely inadequate for the crypto world, which lives an active life 24/7.
As a result, the not very correct positioning of CFDs on crypto led to the fact that the most interested players switched to trading directly on crypto exchanges when the latter offered margin trading.
Choosing the Right CFD Broker to Buy Crypto ( Example Russian Citizens)
Access to the majority of liquid crypto exchanges is currently closed or restricted for citizens of the Russian Federation.
If you want to invest in cryptocurrencies without restrictions, and have options for free withdrawal of profits to a bank card or other medium convenient for you, you need to trade through an international online broker that is not subject to European or Russian sanctions.
Unlike trading CFDs on the stock market and many other markets, there are no time limits for crypto CFDs. With AMarkets you can buy and sell cryptocurrencies at any time of the day and any day of the week.

